Hey there! If you've ever been curious about how the human body is mapped out, you’re in for a treat. In this article, you’ll explore whether the prostate has any anatomical relationship with the bladder. By the end, you'll uncover the fascinating ways these two organs interact and support each other in the intricate dance of human anatomy. So, let’s dive in and discover the connection between the prostate and the bladder.
Does The Prostate Have Any Anatomical Relationship With The Bladder?
Have you ever wondered if the prostate and the bladder are related anatomically? Understanding how these parts of your body interact can offer valuable insights into men's health. In this article, we will dive into the anatomical relationship between the prostate and the bladder, and explore why it's significant.
Introduction
Anatomy can sometimes seem complex, but when you break it down, it becomes easier to understand. Both the prostate and the bladder play crucial roles in bodily functions such as urination and reproduction. Understanding their anatomical relationship can provide deeper insight into various health issues.
What is the Prostate?
The prostate is a small but essential gland in the male reproductive system. Situated just below the bladder, it resembles a walnut in size and shape. Its primary function is to produce seminal fluid, which mixes with sperm to create semen.
What is the Bladder?
The bladder is a muscular sac responsible for storing urine until it’s ready to be excreted. Located in the pelvis, the bladder expands when it is filled and contracts during urination to force the urine out through the urethra.
The Importance of Understanding Their Relationship
The proximity of the prostate and the bladder has significant implications for urinary function and male reproductive health. Conditions affecting one of these organs can often impact the other. By understanding their anatomical relationship, you are better equipped to manage health concerns related to these organs.
Anatomy of the Prostate
Let's take a closer look at the anatomy of the prostate and how it is structured.
Structure of the Prostate
The prostate is a glandular organ composed of both glandular and muscular tissue. It consists of three zones:
- Peripheral Zone
- Central Zone
- Transition Zone
Each of these zones has specific functions and characteristics.
Function of the Prostate
The primary role of the prostate is to produce seminal fluid, which is vital for sperm survival and mobility. Additionally, the prostate contains smooth muscle fibers that help expel semen during ejaculation.
Prostate and Aging
As men age, the prostate undergoes various changes, such as an increase in size. These changes can sometimes result in conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which can affect urinary function.

Anatomy of the Bladder
Now, let's shift our focus to the bladder and understand its anatomy.
Structure of the Bladder
The bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that can hold approximately 400-600 milliliters of urine. It has four main parts:
- Apex
- Body
- Fundus
- Neck
Each of these regions plays a role in the bladder’s ability to store and expel urine.
Function of the Bladder
The bladder’s primary function is to store urine produced by the kidneys until it is excreted. When the bladder fills to capacity, nerve signals trigger the urge to urinate.
Bladder and Aging
Like the prostate, the bladder also undergoes changes with age. Issues such as decreased bladder capacity and increased likelihood of infections become more common.
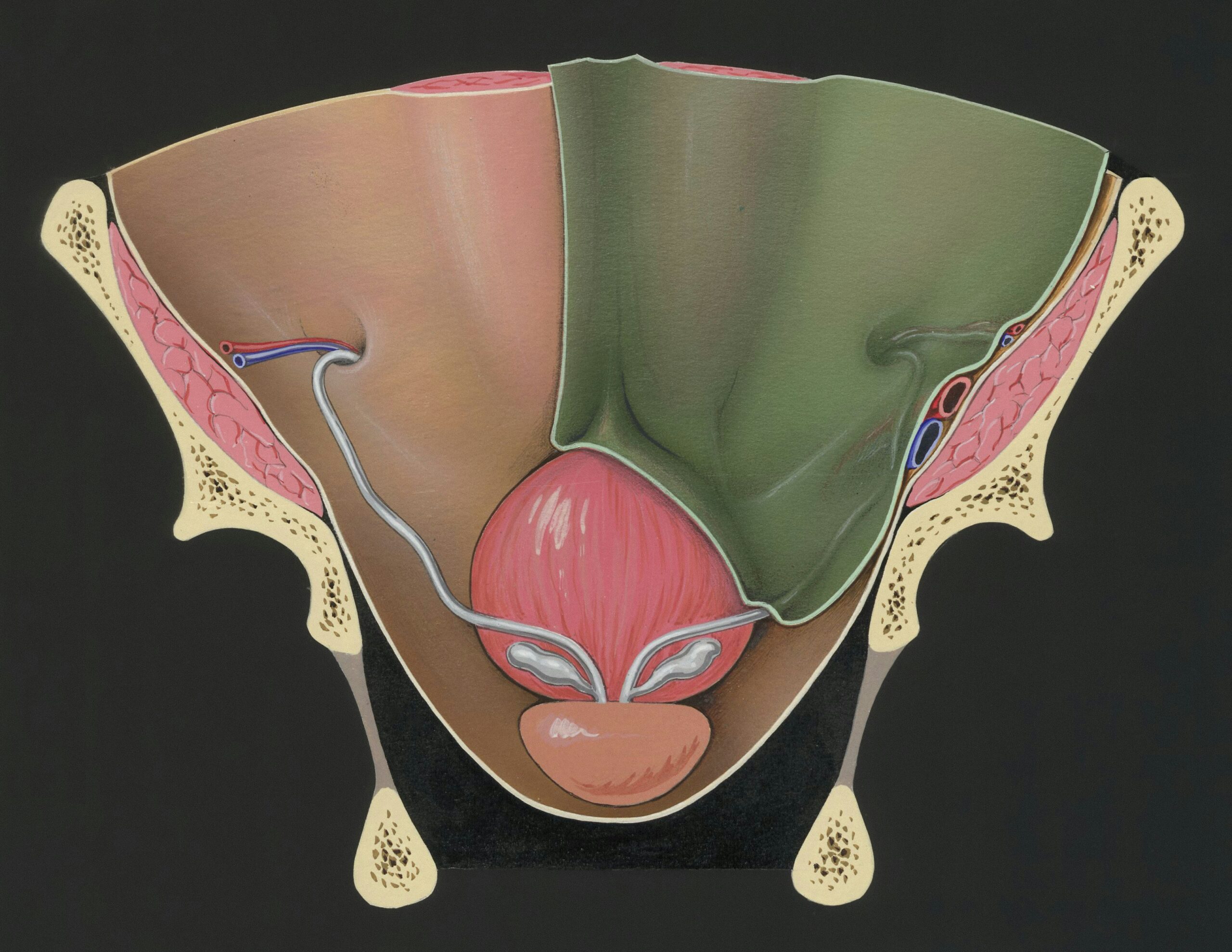
Anatomical Relationship Between the Prostate and the Bladder
Understanding the relationship between the prostate and the bladder involves examining how these organs are positioned relative to one another and how they interact.
Relative Positions
The prostate is located directly below the bladder, encircling the urethra. This close anatomical relationship means that changes in one organ can significantly affect the other.
Table 1 below summarizes the relative positions and significant points of interaction between the prostate and the bladder:
| Organ | Relative Position | Significant Point of Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Bladder | Above the prostate | Urethra exits bladder and passes through the prostate |
| Prostate | Below the bladder | Encircles the urethra |
Urethra and Its Pathway
The urethra, which is responsible for expelling urine from the body, passes through the prostate before reaching the penis. This pathway is crucial for urinary and reproductive functions.
Impact of Prostatic Enlargement
When the prostate enlarges (a condition known as BPH), it can compress the urethra. This compression can lead to difficulties in urination, such as increased frequency, urgency, and incomplete emptying of the bladder.

Health Implications of the Prostate and Bladder Relationship
Understanding the anatomical relationship between the prostate and bladder can help us better comprehend various health issues.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
BPH is a common condition in aging men. It involves the enlargement of the prostate gland, which can compress the urethra and obstruct urinary flow. Understanding the anatomical relationship helps in diagnosing and treating BPH.
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer originates in the prostate gland and can spread to nearby organs, including the bladder. Early detection and understanding of the gland's anatomy can facilitate effective treatment.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Men with prostate issues are more susceptible to UTIs because the connection between the bladder and prostate can facilitate the spread of bacteria. Proper understanding can lead to better management and prevention of infections.
Diagnostic and Treatment Approaches
Understanding the prostate and bladder's anatomical relationship can also guide effective diagnostic and treatment approaches.
Diagnostic Techniques
Several diagnostic techniques can help evaluate the health of the prostate and bladder:
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A physician can feel the size and shape of the prostate by inserting a gloved finger into the rectum.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Measures PSA levels in the blood to detect prostate issues.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the bladder and prostate.
- Cystoscopy: A camera-equipped tube is inserted through the urethra to visualize the bladder and prostate.
Treatment Options
Depending on the condition, various treatment options can be considered:
- Medications: Drugs like alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors can help manage symptoms of BPH.
- Surgery: Procedures like Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) can relieve urinary obstruction.
- Radiation Therapy: Often used for prostate cancer, this method uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
Preventative Measures
Understanding the prostate and bladder relationship can also help in preventive measures to maintain optimal health.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can mitigate the risks of prostate and bladder issues:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake to ensure proper urinary function.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity to improve overall health.
Regular Screenings
Regular screenings and check-ups can aid in the early detection of issues, facilitating timely treatment.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding the prostate and bladder. Let's clear up some of these misunderstandings.
Myth: Prostate Issues Only Affect Older Men
While age is a significant factor, younger men can also experience prostate issues. Regular check-ups are essential, irrespective of age.
Myth: Difficulty Urinating is Always Due to Prostate Problems
While prostate issues frequently cause urinary difficulties, other factors such as bladder infections and neurological conditions can also play a role.
Myth: Surgery is the Only Treatment for Prostate Problems
Surgery is one option among many. Medications and lifestyle modifications can also effectively manage some conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
As we dive deeper into the relationship between the prostate and bladder, you might have some lingering questions. Here, we'll address some frequently asked questions.
What are the early signs of prostate problems?
Early signs can include difficulty urinating, a frequent urge to urinate, and discomfort in the pelvic area. If you notice these symptoms, it's essential to seek medical advice.
Can prostate issues lead to bladder problems?
Yes, prostate issues, particularly BPH, can lead to bladder problems by obstructing urinary flow and increasing the risk of infections.
How can I maintain a healthy prostate and bladder?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, and regular screenings can contribute to the overall health of your prostate and bladder.
Is it normal to have an enlarged prostate as you age?
Yes, it is relatively common for the prostate to enlarge with age. While it is often benign, medical evaluation is crucial to rule out serious conditions like prostate cancer.
Do I need to see a specialist for prostate and bladder issues?
Primary care physicians can handle many issues, but urologists specialize in urinary and reproductive health and may be consulted for more complex conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding the anatomical relationship between the prostate and the bladder provides valuable insights into their functioning and the health implications associated with both organs. The close proximity of these organs means that issues affecting one can often impact the other. By staying informed and proactive, you can take the necessary steps to maintain your prostate and bladder health.
Feel free to ask any other questions you may have about this topic. Your health is important, and staying informed is the first step towards maintaining it.

