You may have heard of a swollen prostate, but do you know what actually causes it? This article will provide you with a concise explanation of the factors that contribute to a swollen prostate. Whether it's age, hormones, or underlying medical conditions, understanding the root causes can help you take proactive steps towards maintaining your prostate health. So, let's uncover the reasons behind a swollen prostate and gain a better understanding of this common issue that affects many men.
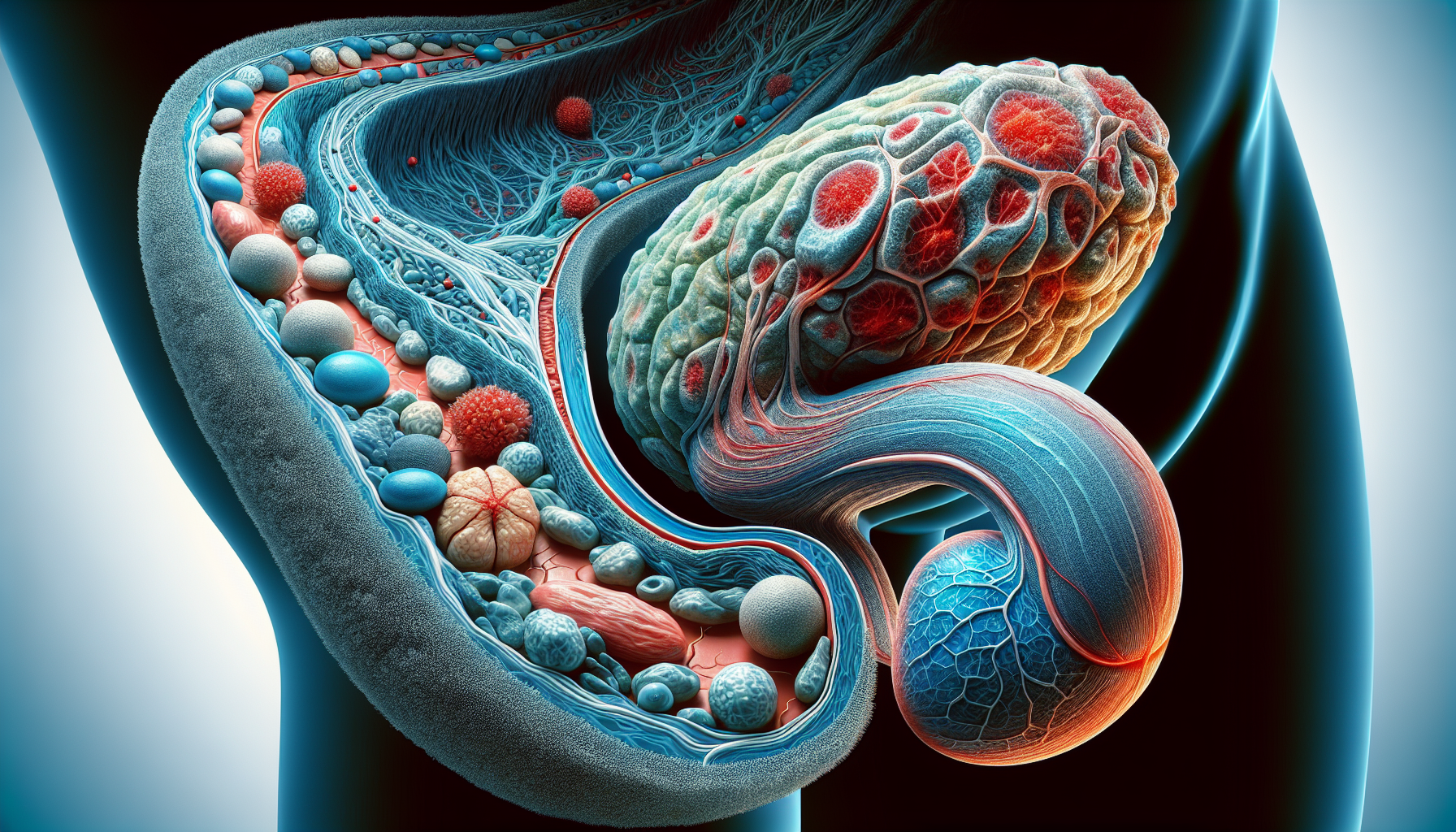
Understanding the Prostate Gland
Function of the prostate
The prostate gland is an important part of the male reproductive system and it plays a crucial role in the production of semen. One of the main functions of the prostate is to secrete a fluid that nourishes and protects the sperm, allowing them to survive and function properly. This fluid is released into the urethra during ejaculation and mixes with sperm from the testicles and other fluids from the seminal vesicles to form semen.
Location and composition of the prostate
The prostate gland is located just below the bladder, surrounding the urethra. It is roughly the size of a walnut and has a unique composition. The majority of the prostate is made up of glandular tissue, which produces the seminal fluid. It also contains muscle fibers that help propel the semen out of the body during ejaculation.
The role of the prostate in the male reproductive system
The prostate gland is a vital component of the male reproductive system. Its main role is to produce the fluid that carries and nourishes the sperm. Without the prostate, the sperm would not be able to survive or move properly, significantly impacting fertility. Additionally, the prostate helps control the flow of urine by surrounding the urethra and providing support to the bladder and urethral sphincters.
Medical Conditions leading to Swollen Prostate
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, or BPH, is a common condition that results in the enlargement of the prostate gland. As the prostate grows larger, it can put pressure on the urethra, leading to symptoms such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and weak urine flow.
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland and can be caused by either bacterial or non-bacterial factors. This condition can cause swelling and discomfort in the prostate, leading to symptoms such as pain during urination, urinary urgency, and pelvic pain.
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a malignant tumor that can develop within the prostate gland. While not all cases of prostate cancer lead to a swollen prostate, the growth of a tumor within the gland can cause enlargement and compression of the urethra, leading to urinary symptoms.
Prostate Infarction
Prostate infarction occurs when there is a blockage of the blood supply to the prostate gland. This can result in tissue death and inflammation, leading to a swollen prostate. Prostate infarction is a rare condition but can cause severe symptoms such as pain, difficulty urinating, and blood in the urine.

Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Definition of BPH
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, commonly known as BPH, is the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. While the exact cause of BPH is still unknown, it is believed to be related to hormonal changes and age. BPH is a common condition in older men and can significantly impact their quality of life.
Relationship between BPH and swollen prostate
BPH directly leads to the swelling of the prostate gland. As the prostate grows larger, it compresses the urethra, restricting the flow of urine. This can result in urinary symptoms such as increased frequency, weak urine flow, difficulty initiating urination, and the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
Prevalence of BPH in men of different ages
BPH is more commonly observed in older men, with the prevalence increasing with age. It is estimated that more than 50% of men in their 60s and over 80% of men in their 80s have some degree of BPH. However, it is important to note that BPH is not always symptomatic and may not require treatment unless it causes significant discomfort or interferes with daily life.
Causes of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Hormonal changes with age
One of the primary factors contributing to the development of BPH is hormonal changes that occur with age. As men age, the balance of hormones, particularly the male sex hormone testosterone and the enzyme called 5-alpha reductase, can shift. This hormonal imbalance can promote the growth and enlargement of the prostate gland.
Genetic predisposition of BPH
There is evidence to suggest that genetics may play a role in the development of BPH. Studies have shown that men with a family history of BPH are more likely to develop the condition themselves. Genetic variations may influence the hormonal regulation or cell growth processes in the prostate gland, leading to the development of BPH.
Lifestyle factors influencing BPH Development
Certain lifestyle factors have been linked to an increased risk of developing BPH. Obesity, lack of physical activity, and a diet high in fat and red meat have been associated with a higher incidence of BPH. Conversely, a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet may help reduce the risk of BPH.
Prostatitis and Swollen Prostate
Understanding Prostatitis
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland and can cause significant discomfort and urinary symptoms. It can be classified into several different types, including acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic pelvic pain syndrome, and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis.
Types of Prostatitis
Acute bacterial prostatitis is caused by a bacterial infection and usually presents with sudden onset symptoms such as fever, chills, urinary urgency, and pain in the pelvic region. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a recurring infection of the prostate that can cause similar symptoms but with milder intensity. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is the most common form of prostatitis and is characterized by chronic pelvic pain, discomfort, and urinary symptoms. Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis does not cause symptoms but is diagnosed incidentally during medical investigations for other conditions.
How does Prostatitis lead to a swollen prostate
Prostatitis can cause the prostate gland to become swollen and tender due to inflammation. The inflammation can disrupt the normal function of the prostate, leading to urinary symptoms and discomfort. In some cases, the swelling caused by prostatitis can also contribute to the development of other conditions such as BPH.
Causes of Prostatitis
Bacterial infection
Acute bacterial prostatitis and chronic bacterial prostatitis are primarily caused by a bacterial infection. Bacteria can enter the prostate through the urethra or bloodstream, leading to infection and inflammation. Common bacteria that cause prostatitis include Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Klebsiella. Sexual activity, urinary tract infections, and catheter use can increase the risk of bacterial prostatitis.
Physical injury to the prostate
Physical injury to the prostate, such as trauma from medical procedures or direct impact during sports activities, can cause inflammation and swelling of the prostate gland. This can lead to prostatitis and subsequent urinary symptoms.
Nonbacterial causes of Prostatitis
In some cases, prostatitis occurs without a bacterial infection. This is known as nonbacterial prostatitis. The exact causes of nonbacterial prostatitis are not well-understood, but it is believed to result from an autoimmune reaction, nerve irritation, or inflammation without a specific infectious agent.
Prostate Cancer and Swollen Prostate
Relationship between prostate cancer and swollen prostate
Prostate cancer can lead to a swollen prostate, especially in advanced stages. As the cancerous cells grow and multiply within the prostate gland, they can cause enlargement and compression of the urethra. This can result in urinary symptoms similar to those seen in BPH.
Prevalence of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men worldwide. The risk of developing prostate cancer increases with age, and it is more commonly seen in men over the age of 50. However, it is important to note that not all cases of prostate cancer lead to a swollen prostate or noticeable symptoms. Regular screening and early detection are crucial for effective management and treatment of prostate cancer.
Risk Factors of Prostate Cancer
Genetic predisposition
There is a significant genetic component to prostate cancer. Men with a family history of prostate cancer, particularly in first-degree relatives such as fathers or brothers, have a higher risk of developing the disease. Genetic variations in certain genes, such as the BRCA2 gene, have also been associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer.
Lifestyle and environmental Risk Factors
Several lifestyle and environmental factors have been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer. These include a diet high in saturated fats, obesity, lack of physical activity, smoking, and exposure to certain chemicals and toxins. Conversely, a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of harmful substances may help reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
Association between Age and Prostate Cancer
Age is the most significant risk factor for prostate cancer. The risk of developing the disease increases significantly after the age of 50, and the majority of prostate cancer cases are diagnosed in men over the age of 65. It is important for men in this age group to undergo regular prostate cancer screening to detect the disease early when it is most treatable.

Other Less Common Causes of Swollen Prostate
Prostate Infarction
Prostate infarction is a rare condition that occurs when the blood supply to the prostate gland is blocked. This can lead to tissue death and inflammation, resulting in a swollen prostate. Prostate infarction is often caused by blood clots or thrombosis and can cause severe symptoms such as pain, difficulty urinating, and blood in the urine.
Drug induced Prostate Swelling
Certain medications, such as certain antihistamines and decongestants, can cause prostate swelling as a side effect. These medications can interfere with the normal function of the prostate gland and lead to symptoms similar to those seen in BPH.
Effects of certain surgical procedures on the prostate
Certain surgical procedures, such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or prostate biopsy, can cause temporary swelling and inflammation of the prostate gland. This can result in urinary symptoms and discomfort, but the swelling usually subsides with time.
Preventing and Managing Swollen Prostate
Lifestyle changes
Certain lifestyle changes can help prevent or manage a swollen prostate. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, reducing caffeine intake, and staying hydrated are all beneficial for prostate health. Additionally, practicing safe sex and maintaining good hygiene can help reduce the risk of bacterial prostatitis.
Medical treatment options
Medical treatment options for a swollen prostate vary depending on the underlying cause. For BPH, medications such as alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors may be prescribed to relieve symptoms and reduce the size of the prostate. In more severe cases, surgical procedures such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or laser ablation may be recommended. Prostatitis may be treated with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms.
Alternative remedies
Some men may seek alternative remedies for managing a swollen prostate. Saw palmetto, a herb commonly used for prostate health, may provide relief from BPH symptoms in some individuals. Other natural remedies, such as beta-sitosterol, pygeum africanum, and rye grass pollen extract, have also shown potential therapeutic effects. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any alternative remedies, as their efficacy and safety may vary for each individual.
In conclusion, a swollen prostate can be caused by various medical conditions such as BPH, prostatitis, prostate cancer, and prostate infarction. Understanding the causes and risk factors of these conditions is essential for prevention and management. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, seeking medical advice for symptoms, and undergoing regular screenings can help ensure the overall health and well-being of the prostate gland.