Are you curious about what benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) really is? BPH refers to the condition where the prostate gland in a man's body grows and becomes larger than normal. This enlargement can lead to various urinary symptoms, such as frequent urination, weak urine flow, and the constant urge to urinate. In this article, we will explore the details of what BPH is and its implications for those affected by it. So, let's dive right in and discover more about this condition together!
Understanding Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Definition of BPH
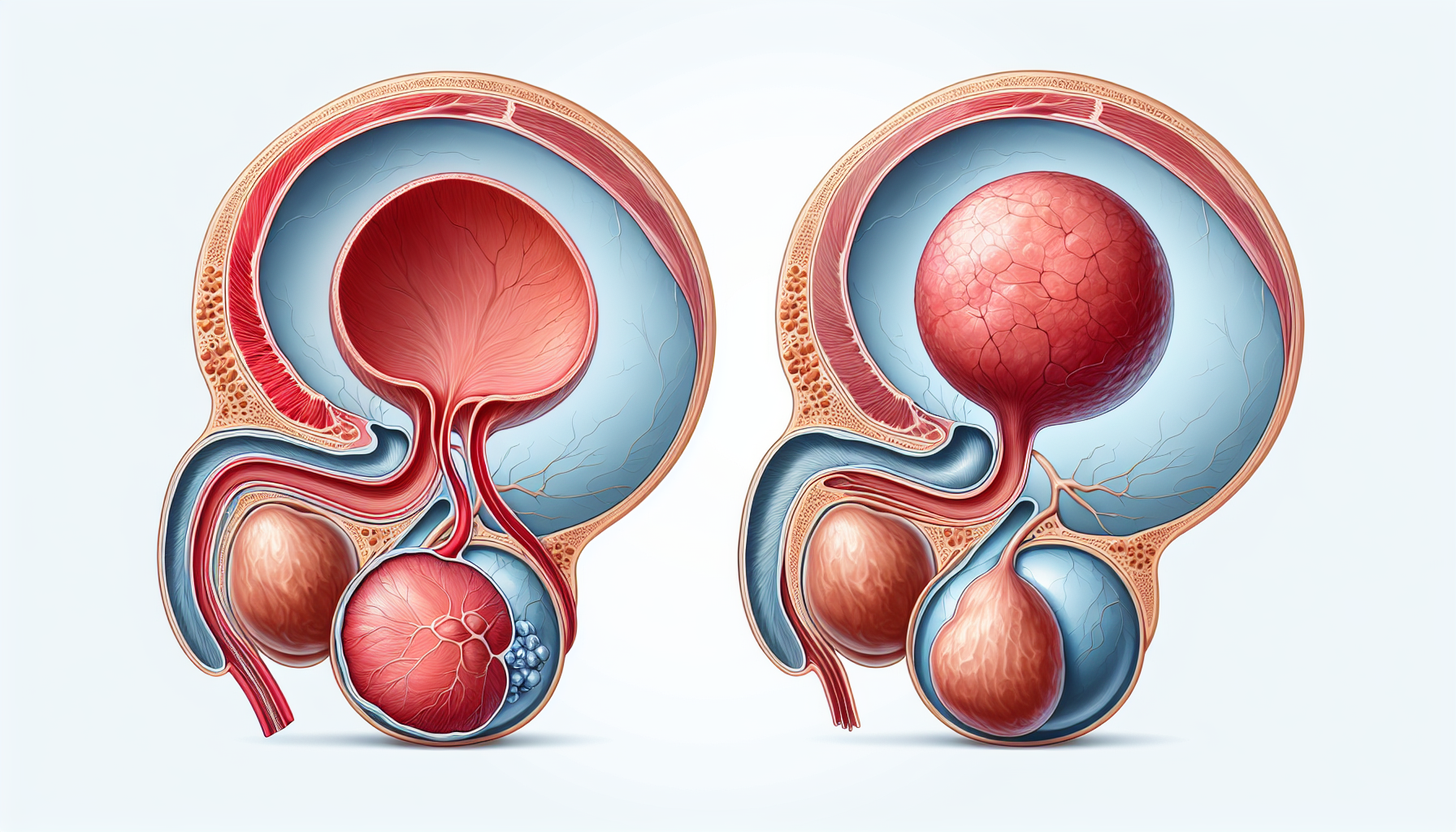
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) refers to the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. The prostate gland, located below the bladder and surrounding the urethra, plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system. As men age, the prostate gland naturally grows larger, and in some cases, this growth can lead to BPH. This condition is also known as benign prostatic hypertrophy.
Understanding the term ‘benign'
In the context of BPH, the term ‘benign' refers to the non-cancerous nature of the condition. While BPH can cause discomfort and inconvenience, it is not associated with prostate cancer. Understanding this distinction is important as it helps relieve anxiety and prevents unnecessary panic among individuals diagnosed with BPH.
Understanding the term ‘prostatic hyperplasia'
The term ‘prostatic hyperplasia' refers to the abnormal increase in the number of cells within the prostate gland, leading to its enlargement. This excessive cell growth occurs mainly in the inner part of the prostate, which surrounds the urethra. As a result, the enlarged prostate can squeeze the urethra, causing various urinary symptoms.
Prevalence of BPH
BPH in younger men
While BPH is more commonly observed in older men, it is not entirely unheard of in younger men as well. Although the likelihood of developing BPH increases with age, some younger men may still experience prostate enlargement. In such cases, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate management strategies.
BPH in older men
BPH is particularly prevalent in older men. As mentioned earlier, the prostate gland naturally grows larger with age, and this age-related enlargement can contribute to the development of BPH. Studies have shown that approximately 50% of men over the age of 50 and up to 90% of men over the age of 80 experience symptoms of BPH. This high prevalence highlights the importance of understanding and managing this condition effectively.
Geographical disparity in BPH prevalence
Interestingly, there seems to be a geographical disparity in the prevalence of BPH. Some studies suggest that BPH is more common in Western countries compared to Asian countries. The exact causes for this difference are not yet fully understood, and further research is needed to explore the potential factors contributing to this variation.
Causes of BPH
Role of hormones in BPH
Hormones, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), have been identified as a primary driver for the development of BPH. As men age, the balance of hormones, including testosterone and estrogen, undergoes changes, leading to an accumulation of DHT in the prostate gland. This accumulation stimulates the growth of prostate cells, resulting in the enlargement observed in BPH.
Genetic link in BPH
Genetics also play a role in the development of BPH. Studies have shown that men with a family history of BPH are more likely to develop the condition themselves. The exact genes responsible for BPH susceptibility are still under investigation, but understanding the genetic component can help identify individuals who may be at a higher risk and allow for proactive measures.
Impact of lifestyle factors on BPH
Several lifestyle factors have been identified as potential contributors to the development and progression of BPH. These include obesity, lack of physical activity, smoking, and a poor diet. While lifestyle factors alone may not be the sole cause of BPH, adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage and potentially prevent the onset of this condition.
Symptoms of BPH
Lower urinary tract symptoms
The most common symptoms associated with BPH are those related to lower urinary tract dysfunction. These include frequent urination, urgency to urinate, weak urine flow, difficulty initiating urination, and a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, causing discomfort and inconvenience.
Sexual dysfunction symptoms
In addition to lower urinary tract symptoms, BPH can also lead to sexual dysfunction. Some individuals with BPH may experience erectile dysfunction, reduced sexual desire, and difficulty ejaculating. These symptoms can have emotional and relational implications, further emphasizing the importance of understanding and managing BPH effectively.
Perceived impact of BPH symptoms on quality of life
The symptoms of BPH, both urinary and sexual, can have a profound impact on an individual's quality of life. They can disrupt daily activities, affect sleep patterns, and cause emotional distress. It is essential for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek medical attention and discuss potential treatment options to alleviate their impact and improve overall well-being.
Diagnosis of BPH
Medical history and physical examination
To diagnose BPH, healthcare professionals typically begin by taking a detailed medical history, including a discussion of symptoms experienced. This is followed by a physical examination, which may include a digital rectal examination (DRE) to assess the size and condition of the prostate gland. These initial steps help healthcare providers gather essential information for a comprehensive diagnosis.
Lab tests for BPH
Lab tests, such as blood tests and urine analysis, may be conducted to rule out other potential causes for symptoms and assess kidney function. These tests can also provide insights into hormone levels, which can help confirm a diagnosis of BPH.
Imaging techniques used in BPH diagnosis
Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be used to visualize the prostate gland and assess its size and structure. These non-invasive imaging modalities can provide valuable information to aid in the diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Treatment for BPH
Lifestyle changes for managing BPH
In cases of mild to moderate BPH, lifestyle modifications can often play a significant role in symptom management. These changes may include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding bladder irritants (e.g., caffeine and alcohol), and practicing pelvic floor exercises. By making these adjustments, individuals with BPH can potentially alleviate symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Medications used in BPH treatment
There are several medications available to help manage BPH symptoms. These medications work by targeting different aspects of the condition, such as reducing prostate size, relaxing the muscles in the prostate and bladder, and improving urine flow. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable medication based on individual circumstances.
Surgical options for BPH
In cases where lifestyle changes and medications do not provide sufficient relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Various surgical procedures, such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), laser surgery, and prostate artery embolization, can be performed to alleviate urinary symptoms and improve overall urinary function. Surgical options are typically considered for more severe cases of BPH or when other treatment options have been ineffective.
Complications of BPH
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to BPH
BPH can increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to urinary retention and incomplete bladder emptying. When urine remains in the bladder for prolonged periods, it creates an environment conducive to bacterial growth, leading to infection. UTIs can cause additional discomfort and may require antibiotic treatment to resolve.
Bladder stones due to BPH
In some cases, BPH can lead to the formation of bladder stones. When urine is retained in the bladder, minerals and other substances can accumulate, forming solid masses known as bladder stones. These stones can cause pain, urinary difficulties, and may require medical intervention to remove them.
Kidney damage due to BPH
In rare cases, severe or untreated BPH can eventually lead to kidney damage. The obstruction of urine flow caused by an enlarged prostate can cause urine to back up into the kidneys, leading to complications such as kidney infections, kidney stones, and ultimately, kidney damage. Early detection and appropriate management of BPH are crucial in preventing such complications.
Preventing BPH
Dietary changes to prevent BPH
While the exact cause of BPH remains unclear, adopting a healthy diet may contribute to the prevention and management of this condition. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that promote prostate health. Additionally, limiting the consumption of processed foods, red meat, and high-fat dairy products may help reduce the risk of BPH.
Exercise's role in preventing BPH
Regular physical activity has been associated with a reduced risk of BPH. Engaging in activities such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming can help maintain a healthy weight, improve overall cardiovascular health, and potentially reduce the risk of developing BPH. Incorporating exercise into one's daily routine is a beneficial preventive measure for various health conditions, including BPH.
The impact of regular health screenings on early BPH detection
Routine health screenings, including regular prostate exams and discussions about urinary symptoms, can facilitate early detection of BPH. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and management, potentially minimizing the impact of the condition on daily life. It is important for individuals, especially those at higher risk, to prioritize regular health check-ups and establish open communication with their healthcare providers.
Living with BPH
Managing BPH symptoms in daily life
Living with BPH requires implementing strategies to alleviate symptoms and maintain overall well-being. This may involve practicing good bladder habits, such as drinking enough water, avoiding excessive fluid intake before bedtime, and emptying the bladder completely during urination. Additionally, individuals with BPH can benefit from managing stress, engaging in relaxation techniques, and seeking support from healthcare professionals.
Emotional impact of BPH
It is important to recognize and address the emotional impact that BPH can have on individuals. The symptoms and challenges associated with this condition can result in feelings of frustration, embarrassment, and anxiety. Seeking emotional support from loved ones, joining support groups, or seeking counseling can provide a safe space to discuss concerns and help manage the emotional aspects of living with BPH.
Support for individuals with BPH
Various sources of support are available for individuals living with BPH. Healthcare professionals, including urologists, can provide guidance, treatment options, and ongoing monitoring. Additionally, support groups, both in-person and online, connect individuals with BPH, allowing them to share experiences, exchange coping strategies, and provide emotional support. It is important for individuals to reach out for support and know that they are not alone in their journey with BPH.
Research On BPH
Recent breakthroughs in BPH research
Advancements in BPH research have led to several promising breakthroughs. Researchers have identified potential new drug targets, such as phytotherapeutic agents, which are derived from plants and have shown promising effects in reducing prostate size and relieving BPH symptoms. Other areas of research focus on novel surgical techniques and a better understanding of the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying BPH development.
Ongoing clinical trials on BPH
Clinical trials are underway to explore new treatment options and further enhance our understanding of BPH. These trials aim to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of innovative medications, minimally invasive procedures, and combination therapies for managing BPH. By participating in clinical trials, individuals with BPH can contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge and potentially benefit from cutting-edge treatments.
Future prospects and current challenges in BPH research
While progress has been made, challenges still exist in BPH research. The complexity of the condition, the need for better diagnostic tools, and the identification of targeted therapies remain significant areas of focus. However, with continued research efforts and collaborations between scientists, clinicians, and patients, the future holds promise for improved prevention, diagnosis, and treatment options for individuals living with BPH.